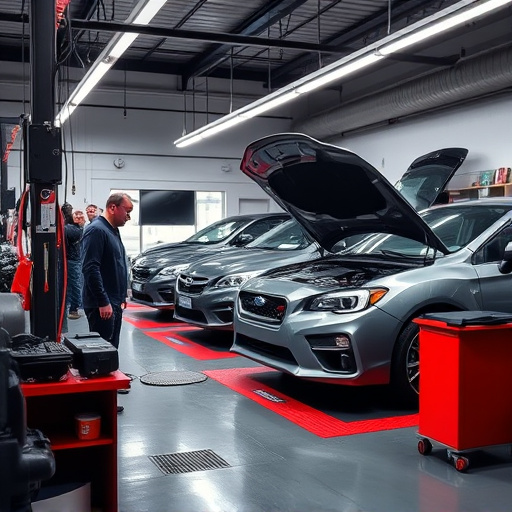
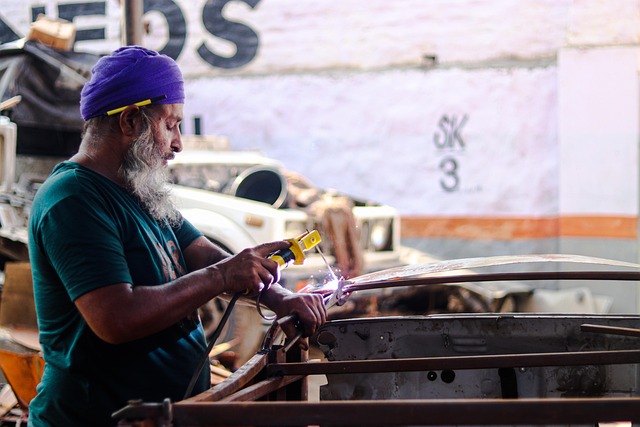
Structural Integrity Restoration (SIR) is a meticulous process that strengthens and repairs damaged structures, preserving their historical value while meeting modern safety standards, particularly in vehicle restoration. Beyond waste reduction, SIR promotes habitat creation and biodiversity by transforming unsalvageable buildings into homes for local ecosystems. This eco-friendly approach, applicable to industries like auto collision repair, requires careful planning, utilizing green materials, efficient waste management, and innovative techniques to minimize environmental impact and carbon emissions in urban settings.
“Uncovering the profound environmental implications of Structural Integrity Restoration (SIR) is essential in our pursuit of sustainable practices. This article explores the transformative power of SIR, a process that goes beyond mere construction. By understanding its definition and relevance, we uncover significant positive impacts, from waste reduction to habitat creation. We also delve into challenges, emphasizing the need for sustainable considerations in restoration projects, ensuring a balanced approach to environmental stewardship.”
- Understanding Structural Integrity Restoration: A Definition and Its Relevance
- The Positive Environmental Impacts: From Reduced Waste to Habitat Creation
- Challenges and Considerations: Ensuring Sustainable Practices in Restoration Projects
Understanding Structural Integrity Restoration: A Definition and Its Relevance

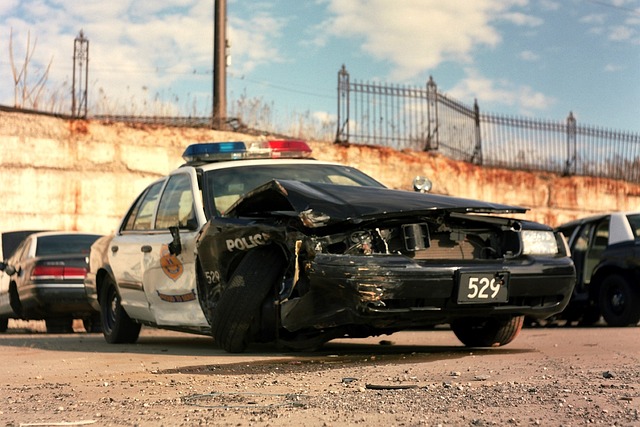
Structural Integrity Restoration (SIR) is a critical process that focuses on reinforcing and repairing damaged structures to ensure their long-term stability and safety. It involves meticulous techniques to enhance the structural integrity of various elements, from buildings to vehicles. In the context of vehicle restoration, SIR plays a pivotal role in bringing old cars back to life while maintaining their historical value.
This process goes beyond mere fender repair or vehicle bodywork restoration; it delves into reinforcing frames, replacing weakened components, and ensuring every part meets the required safety standards. By adopting SIR practices, professionals can preserve vintage vehicles, making them not just visually appealing but also structurally sound for modern use. This attention to detail is essential in industries where both aesthetics and functionality are paramount, such as classic car collections or specialty vehicle restoration projects.
The Positive Environmental Impacts: From Reduced Waste to Habitat Creation

The environmental benefits of structural integrity restoration extend far beyond simply reducing damage to buildings and infrastructure. By focusing on repairing and reinforcing structures rather than replacing them, significant amounts of construction waste are avoided. This is particularly notable in urban areas where space for landfills is limited and the pressure to recycle or reuse materials is high.
Moreover, structural integrity restoration can contribute to habitat creation and biodiversity. Many restored buildings and structures, especially those once considered unsalvageable, can be transformed into homes for various species of birds, insects, and small animals. This process not only enhances local ecosystems but also increases the overall resilience of these habitats against future environmental challenges, mirroring the principles of sustainable auto collision repair and auto body repair in a broader urban context, including vehicle body shop operations.
Challenges and Considerations: Ensuring Sustainable Practices in Restoration Projects

Restoring structural integrity is a complex process that demands meticulous planning and execution to minimize environmental impact. Challenges arise from the need to balance historical preservation with modern sustainability goals, especially in urban areas where space is limited. Restoration projects must consider the use of eco-friendly materials, efficient waste management strategies, and innovative techniques to reduce energy consumption during both construction and operation phases.
Additionally, collision repair services for auto glass and car structural components contribute to the complexity. Integrating these repairs seamlessly into restoration plans ensures that the overall environmental footprint remains as small as possible. Proper disposal of hazardous waste from car accidents, such as fluids and metals, is crucial. Employing recycled materials and implementing green building practices can significantly offset the carbon footprint associated with both the collision repair services and structural integrity restoration processes.
Structural integrity restoration, while demanding careful navigation, emerges as a powerful tool for mitigating environmental degradation. By prioritizing sustainable practices, this method not only ensures the longevity of built structures but also contributes to habitat creation and waste reduction. As we continue to navigate the challenges posed by climate change, embracing structural integrity restoration can play a pivotal role in fostering more resilient and eco-friendly communities.